EIA updates 2022, 2023 bioenergy forecasts
Energy Disrupter
ADVERTISEMENT
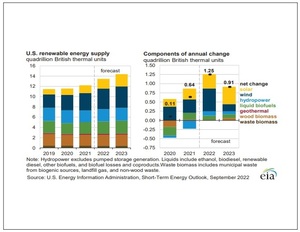
Renewables are expected to provide 22 percent of U.S. electricity generation this year, increasing to 24 percent in 2023, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s latest Short-Term Energy Outlook. Renewable accounted for 20 percent of U.S. electricity generation last year.
The electric power sector generated 27.9 billion kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity from biomass last year, including 12.5 billion kWh from waste biomass and 12.4 billion kWh from wood biomass. Biomass generation is expected to fall to 26.7 billion kWh in 2022, including 14.5 billion kWh from waste biomass and 12.2 billion kWh from wood biomass. Biomass generation is expected to further decline in 2023, falling to 26.1 billion kWh, with waste biomass generation maintained at 14.5 billion kWh and wood biomass generation falling to 11.5 billion kWh.
Across other sectors, biomass generation is expected to be at 27.4 billion kWh this year, including 2.8 billion kWh from waste biomass and 24.5 billion kWh from wood biomass. Those levels of generation are expected to be maintained through 2023. Biomass generation was at 27.6 billion kWh last year, including 2.8 billion kWh from waste biomass and 24.8 billion kWh from wood biomass.
The electric power sector is expected to consume 0.221 quadrillion Btu (quad) of waste biomass in both 2022 and 2023, down from 0.236 quad in 2021. The sector is also expected to consume 0.195 quad of wood biomass this year, falling to 0.183 quad in 2023. The sector consumed 0.199 quad of wood biomass in 2021.
The industrial sector is expected to consume 0.163 quad of waste biomass in 2022, falling to 0.161 quad in 2023. The sector consumed 0.16 quad of waste biomass last year. The sector is also expected to consume 1.335 quad of wood biomass this year, increasing to 1.404 quad in 2023. Consumption of wood biomass was at 1.342 quad in 2021.
The commercial sector is expected to consume 0.037 quad of waste biomass in both 2022 and 2023, up from 0.035 quad in 2021. The sector consumed 0.083 quad of wood biomass last year, with that level of consumption expected to be maintained through 2022 and 2023.
The residential sector is expected to consume 0.474 quad of wood biomass in both 2022 and 2023, up from 0.764 quad in 2021.
Across all sectors, waste biomass consumption is expected to reach 0.421 quad this year, falling to 0.419 quad next year. Consumption was at 0.431 quad in 2021. Wood biomass consumption was at 2.087 quad last year. Consumption is expected to continue at that level this year before increasing to 2.144 quad in 2023.
The electric power sector had 5,933 megawatts (MW) of biomass capacity at the end of 2021, including 3,631 MW of waste biomass capacity and 2,303 MW of wood biomass capacity. Biomass capacity is expected to fall to 5,868 MW by the end of this year, including 3,566 MW of waste biomass capacity and 2,303 MW of wood biomass capacity. Biomass capacity is expected to reach 5,874 MW by the end of 2023, including 3,571 MW of waste biomass capacity and 2,303 MW of wood biomass capacity.
Across other sectors, biomass capacity was at 6,014 MW at the end of last year, including 808 MW of waste biomass capacity and 5,206 MW of wood biomass capacity. Biomass capacity is expected to fall slightly to 6,011 MW by the end of this year, including 808 MW of waste biomass capacity and 5,202 MW of wood biomass capacity. Biomass capacity is expected to fall to 6,003 MW by the end of 2023, including 808 MW of waste biomass capacity and 5,194 MW of wood biomass capacity.